12.3.10 - Application of Deep Learning Models to Predict Achievement of PASS at Minimum 2-Year Follow-Up After Primary Hip Arthroscopy
- P. Padilla (Des Plaines, US)
- B. Domb (Des Plaines, US)
- A. Jimenez (Des Plaines, US)
- M. Lee (Des Plaines, US)
- J. Owens (Des Plaines, US)
- D. Maldonado (Des Plaines, US)
- A. Lall (Des Plaines, US)
- T. Harris (Des Plaines, US)
- P. Sabetian (Des Plaines, US)
- P. Padilla (Des Plaines, US)
Abstract
Purpose
To identify predictive factors for achieving PASS in patients undergoing primary hip arthroscopy and labral repair for femoroacetabular impingement syndrome (FAIS) and labral tears.
Methods and Materials
Data were prospectively collected and retrospectively reviewed on all patients undergoing primary hip arthroscopy and labral repair for femoroacetabular impingement syndrome (FAIS) and labral tears between July 2015 and May 2019. The primary outcome was achievement of PASS based on an anchor-question at minimum 2-year follow up. A Multilayer Perceptron Artificial Neural Network (MLP-ANN), Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), and logistic regression models were trained on an independent testing set of patients to identify significant predictors.
Results
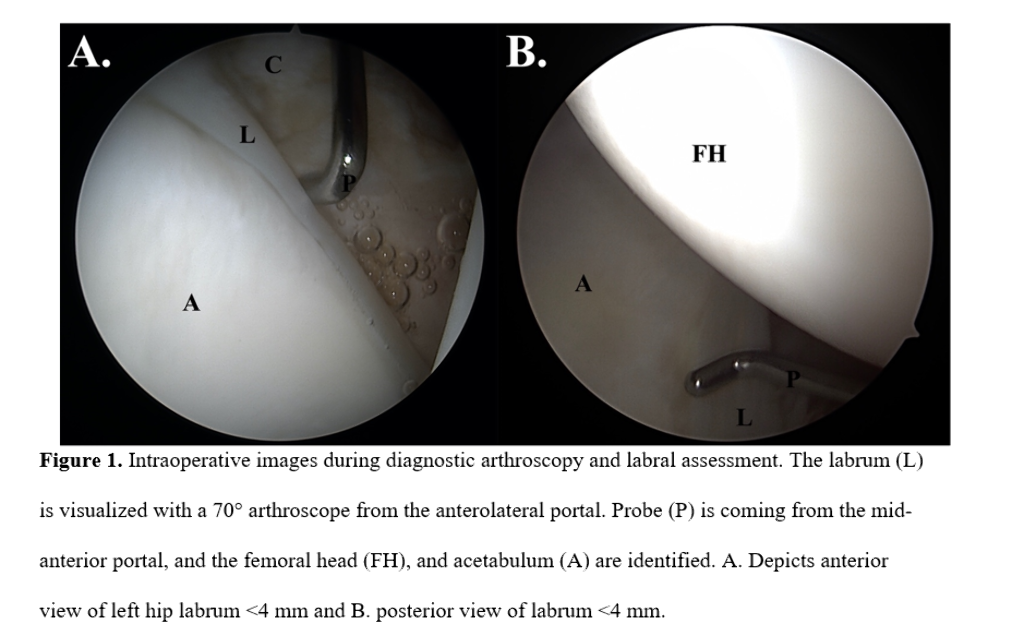
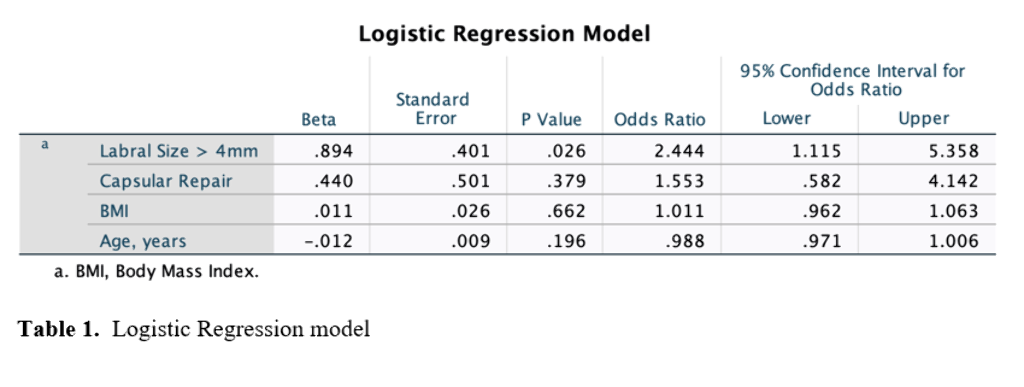
A total of 343 patients were included with 263/343 (76.7%) achieving the PASS threshold at minimum 2-year follow-up. A combination of 4 variables optimized model performance: capsular management (repair vs unrepair of interportal capsulotomy), labral size (<4 mm or ≥4 mm in the anterosuperior quadrant), age (years), and body mass index (BMI). The MLP-ANN model demonstrated the best accuracy (R2 = 78.1%) followed by the logistic regression (R2 = 71.8%) and XGBoost (R2 = 71.3%). The logistic regression found labral size ≥ 4mm to be the only statistically significant variable for predicting achievement of PASS (Odds Ratio: 2.444, P = 0.026). Patients with labral size ≥ 4mm achieved PASS at a rate of 78.7%, and patients with labral size < 4mm achieved PASS at a rate of 59.4% (P = 0.0244).
Conclusion
Labral size, capsular management, age, and BMI were found to be significant predictors of achieving PASS at minimum 2-year follow-up in patients undergoing primary hip arthroscopy and labral repair. Labral size ≥ 4 mm was the most statistically significant factor in favor of achieving PASS in this patient population.