Author Of 1 Presentation
VENTED IONIZATION CHAMBERS FOR ULTRA-HIGH DOSE PER PULS CONDITIONS
Abstract
Background and Aims
Vented ionization chambers (IC) are used as the standard dosimeter for clinical reference dosimetry. For ultra-high dose per pulse (DPP) in the range of 0.6 – 10 Gy, as under investigation for FLASH radiotherapy with electrons, available ICs show large deviations due to ion recombination. However, it is desirable to use ICs also under ultra-high DPP conditions as a secondary standard.
Methods
Parallel plate prototype ICs with different electrode distances d manufactured by PTW were investigated at PTB's research electron accelerator (20 MeV, 5 Hz, 2.5 µs pulse duration). To determine the DPP reference, the beam current monitor was calibrated against alanine. The measurements were compared to a numerical approach by solving a system of partial difference equations, taking into account charge creations by the radiation, their transport and reaction in an applied electric field.
Results
As the electrode distance decreases, the deviations due to ion recombination become smaller. For the prototype with d=0.25mm, almost no deviation is detectable anymore. There is a good agreement between measurements and simulations.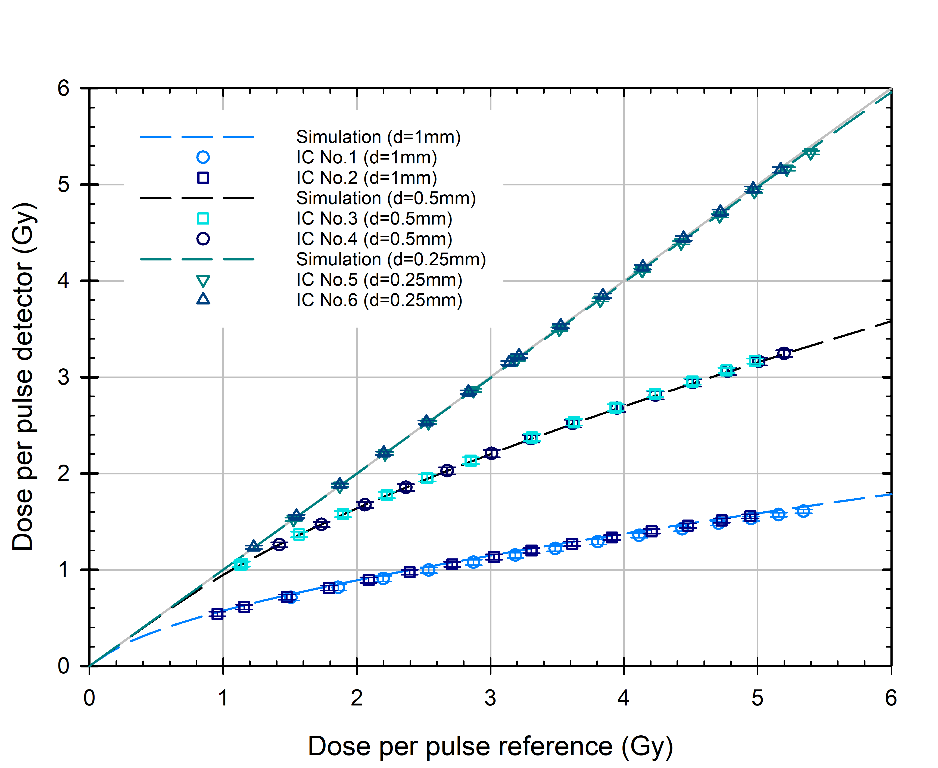
Figure 1: Measured and simulated DPP vs. reference DPP for ICs with different electrode distances d and a voltage of 250V.
Conclusions
Our investigation confirms the previous findings of Gomez et al. presented on this conference. Parallel plate ICs with very small electrode distances are a promising tool for real time dosimetry in FLASH radiotherapy.
Acknowledgement
This project 18HLT04 UHDpulse has received funding from the EMPIR programme co-financed by the Participating States and from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme.

