Belinda D. Ortika, Australia
Murdoch Children's Research Institute Infection and ImmunityPoster Author Of 1 e-Poster
FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH PNEUMOCOCCAL CARRIAGE IN CHILDREN AND ADULTS IN FIJI, USING FOUR CROSS-SECTIONAL SURVEYS
- Eleanor F. Neal, Australia
- Cattram D. Nguyen, Australia
- Felista T. Ratu, Fiji
- Eileen M. Dunne, United States of America
- Lisi Tikoduadua, Fiji
- Mike Kama, Fiji
- Belinda D. Ortika, Australia
- Laura K. Boelsen, Australia
- Joseph Kado, Australia
- Rachel Devi, Fiji
- Evelyn Tuivaga, Fiji
- Rita C. Reyburn, Australia
- Catherine Satzke, Australia
- Eric Rafai, Fiji
- Kim E. Mulholland, Australia
- Fiona M. Russell, Australia
Author Of 8 Presentations
IMMUNOGENICITY OF A SINGLE DOSE OF PCV10 GIVEN AT 18 MONTHS OF AGE AND IMPACT ON NASOPHARYNGEAL CARRIAGE IN VIETNAMESE CHILDREN (ID 735)
- Rachel A. Marimla, Australia
- Beth Temple, Australia
- Thi Trang Dai Vo, Viet Nam
- Thanh V. Phan, Viet Nam
- Trong Toan Nguyen, Viet Nam
- Leena Spry, Australia
- Monica L. Nation, Australia
- Belinda D. Ortika, Australia
- Doan Y. Uyen, Viet Nam
- Cattram D. Nguyen, Australia
- Kathryn Bright, Australia
- Anne Balloch, Australia
- Huu T. Ngoc, Viet Nam
- Kim E. Mulholland, Australia
- Catherine Satzke, Australia
- Paul V. Licciardi, Australia
FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH PNEUMOCOCCAL CARRIAGE IN CHILDREN AND ADULTS IN FIJI, USING FOUR CROSS-SECTIONAL SURVEYS (ID 224)
- Eleanor F. Neal, Australia
- Cattram D. Nguyen, Australia
- Felista T. Ratu, Fiji
- Eileen M. Dunne, United States of America
- Lisi Tikoduadua, Fiji
- Mike Kama, Fiji
- Belinda D. Ortika, Australia
- Laura K. Boelsen, Australia
- Joseph Kado, Australia
- Rachel Devi, Fiji
- Evelyn Tuivaga, Fiji
- Rita C. Reyburn, Australia
- Catherine Satzke, Australia
- Eric Rafai, Fiji
- Kim E. Mulholland, Australia
- Fiona M. Russell, Australia
Abstract
Background
We describe factors associated with pneumococcal nasopharyngeal carriage in Fiji, using data from annual (2012-2015) cross-sectional surveys, pre- and post-introduction of ten-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV10).
Methods
Infants (5-8 weeks), toddlers (12-23 months), children (2-6 years), and their caregivers participated. Pneumococci were detected using lytA qPCR, with molecular serotyping by microarray. We used logistic regression to determine predictors of pneumococcal carriage.
Results
There were 8,109 participants. Pneumococcal carriage was associated with: years post-PCV10 introduction (global P<0.001), indigenous iTaukei ethnicity (aOR 2.74 [95% CI 2.17-3.45] P<0.001); young age (global P<0.001); urban residence (aOR 1.45 [95% CI 1.30-2.57] P<0.001); living with >2 children <5 years (aOR 1.42 [95% CI 1.27-1.59] P<0.001); poverty (aOR 1.44 [95% CI 1.28-1.62] P<0.001); and upper respiratory tract infection symptoms (aOR 1.77 [95% CI 1.57-2.01] P<0.001). Factors associated with PCV10 and non-PCV10 carriage were similar to those associated with overall carriage. Additionally, PCV10 carriage was associated with PCV10 vaccination (0.58 [95% CI 0.41-0.82] P=0.002) and cigarette smoke exposure (aOR 1.21 [95% CI 1.02-1.43] P=0.031, while non-PCV10 carriage was not associated with years post-PCV10 introduction.
Conclusions
Introduction of PCV10 reduced the odds of overall and PCV10 pneumococcal carriage in Fiji. Indigenous iTaukei ethnicity was positively associated with carriage after adjustment for PCV10.
NASOPHARYNGEAL PNEUMOCOCCAL DENSITY IS ASSOCIATED WITH SEVERE PNEUMONIA IN YOUNG CHILDREN IN LAO PDR (ID 856)
- Olivia J. Carr, Australia
- Keoudomphone Vilivong, Laos
- Mimee Laddaphone, Laos
- Eileen M. Dunne, United States of America
- Jana Y. Lai, Australia
- Jocelyn Chan,
- Malisa Vongsakid, Laos
- Chanthaphone Siladeth, Laos
- Belinda D. Ortika, Australia
- Mayfong Mayxay, United Kingdom
- Paul N. Newton, United Kingdom
- Lien Anh Ha H. Do, Australia
- Kim E. Mulholland, Australia
- Audrey Dubot-Pérès, Laos
- Catherine Satzke, Australia
- David A. Dance, Laos
- Fiona M. Russell, Australia
Abstract
Background
Pneumococcal nasopharyngeal colonisation density >6.9 log10 copies/mL is associated with primary endpoint pneumonia, very severe pneumonia and hypoxic pneumonia. Few studies have explored the association between pneumococcal density and severe pneumonia. We determined the association between nasopharyngeal pneumococcal density and children with severe pneumonia in Laos.
Methods
A prospective observational study was conducted at Mahosot Hospital. Children <5 years of age admitted with ARI were recruited (2014 to mid-2018). Clinical and demographic data were collected alongside with nasopharyngeal swabs. Severe pneumonia was classified according to the WHO 2013 definition. Pneumococci were detected and quantified by lytA qPCR. A logistic regression model deterimined the association between pneumococcal density and severe pneumonia, after adjusting for potential confounders.
Results
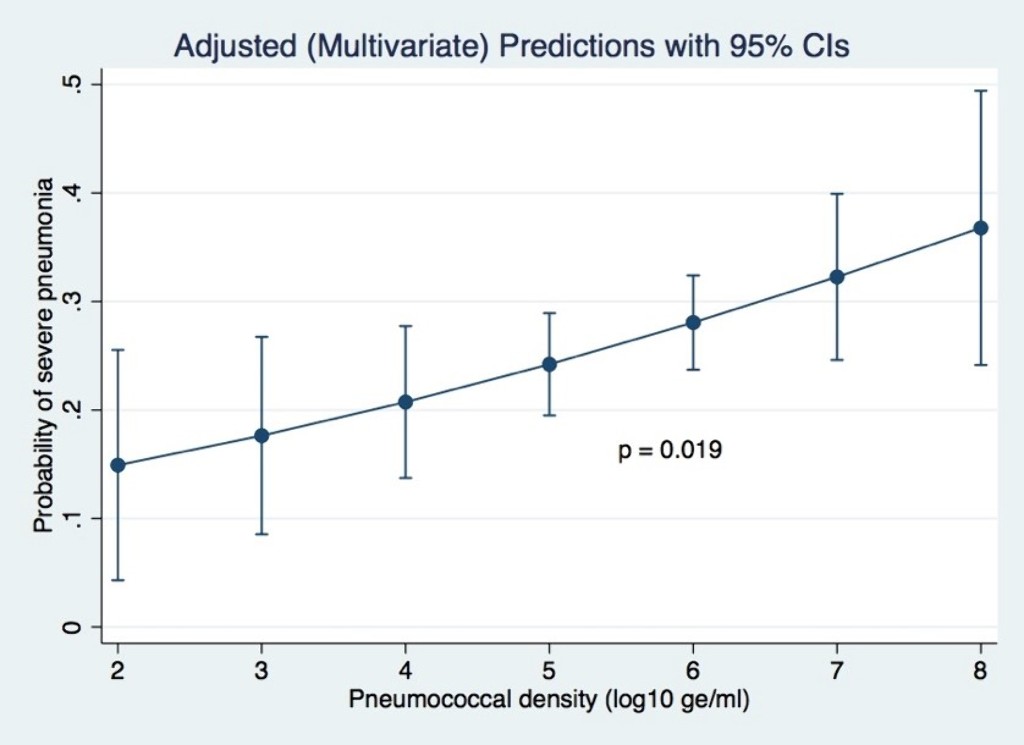
Of 1,289 participants enrolled, 32.2% had severe pneumonia. After adjusting for potential confounders (age, ethnicity, residential location, living with children <5 years, exposure to cigarette smoke, monthly income, PCV13 vaccination status and co-detection of RSV), pneumococcal density was positively associated with severe pneumonia (adjusted odds ratio 1.4; 95% CI 1.1–1.8; p=0.019).
Conclusions
Pneumococcal carriage density is associated with the probability of severe pneumonia in children in this setting.
PNEUMOCOCCAL CARRIAGE PRE- AND POST- PCV: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW (ID 431)
- Nicole Wong, Australia
- Eleanor F. Neal, Australia
- Sam Clifford, United Kingdom
- Belinda D. Ortika, Australia
- Kyla Hayford, United States of America
- Shereen Labib, Australia
- Julia Bennett, United States of America
- Maria D. Knoll, United States of America
- Stefan Flasche, United Kingdom
- Fiona M. Russell, Australia
COMPARISON OF A 2+1 AND 3+0 SCHEDULE OF PCV10 IN VIETNAM (ID 1035)
- Beth Temple, Australia
- Paul V. Licciardi, Australia
- Vo Thi Trang Dai, Viet Nam
- Trong Toan Nguyen, Viet Nam
- Doan Y. Uyen, Viet Nam
- Cattram D. Nguyen, Australia
- Thanh V. Phan, Viet Nam
- Hoan Thi Pham, Viet Nam
- Kathryn Bright, Australia
- Rachel A. Marimla, Australia
- Monica L. Nation, Australia
- Belinda D. Ortika, Australia
- Catherine Satzke, Australia
- Heidi Smith-Vaughan, Australia
- Anne Balloch, Australia
- Tran Ngoc Huu, Viet Nam
- Edward K. Mulholland,
INSIGHTS INTO PNEUMOCOCCAL PNEUMONIA USING LUNG ASPIRATES AND NASOPHARYNGEAL SWABS COLLECTED FROM PNEUMONIA PATIENTS IN THE GAMBIA (ID 668)
PNEUMOCOCCAL CARRIAGE IN CHILDREN WITH PNEUMONIA IN THREE ASIAN COUNTRIES FOLLOWING VACCINE INTRODUCTION (ID 1082)
- Catherine Satzke, Australia
- Eileen M. Dunne, United States of America
- Jocelyn Chan,
- Monica L. Nation, Australia
- Keoudomphone Vilivong, Laos
- Belinda D. Ortika, Australia
- Mimee Laddaphone, Laos
- Rebecca Ford, Papua New Guinea
- Joycelyn J. Sapura, Papua New Guinea
- John Kave, Papua New Guinea
- Cattram D. Nguyen, Australia
- Casey L. Pell, Australia
- Ahmed Alamrousi, Australia
- Jason Hinds, United Kingdom
- Paul N. Newton, United Kingdom
- Anonh Xeuatvongsa, Laos
- B Bunjinlham,
- Christopher C. Blyth, Australia
- David A. Dance, Laos
- William Pomat, Papua New Guinea
- Claire Von Mollendorf, Australia
- Tuya Mungun, Mongolia
- Kim E. Mulholland, Australia
- Fiona M. Russell, Australia
IMPACT OF A SINGLE DOSE OF PCV10 OR PCV13 ON NASOPHARYNGEAL PNEUMOCOCCAL CARRIAGE IN VIETNAMESE CHILDREN DURING THE FIRST YEAR OF LIFE (ID 696)
- Hoan Thi Pham, Viet Nam
- Beth Temple, Australia
- Thi Trang Dai Vo, Viet Nam
- Thanh V. Phan, Viet Nam
- Loc Thuy Ho Nguyen, Viet Nam
- Anh H.V Nguyen,
- Belinda D. Ortika, Australia
- Kathryn Bright, Australia
- Catherine Satzke, Australia
- Nevio D. Sarmento, Timor-Leste
- Jemima Beissbarth, Australia
- Heidi Smith-Vaughan, Australia
- Thuong V. Nguyen, Viet Nam
- Kim E. Mulholland, Australia
Abstract
Background
Reduced-dose schedules of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) could increase the accessibility and use of PCV in low and middle-income countries.
Methods
Groups within the Vietnam Pneumococcal Trial II receive PCV10 and PCV13 in a 1+1 schedule at 2 and 12 months of age, or no vaccine. Nasopharyngeal swabs were collected at 6 and 12 months of age to show the impact of the 2-month dose on pneumococcal carriage.
Results
Based on analysis to date of 1152 of 3200 swabs, vaccine-type carriage was low. In unvaccinated participants, PCV10 and PCV13-type carriage were 5.1% and 10.4% at 6 months, and 8.3% and 12.0% at 12 months, respectively. A dose of PCV10 transiently reduced vaccine-type carriage at 6 months of age (3/178 [1.7%] versus 18/355 [5.1%]).
Conclusions
With the exception of the PCV10 group at 6 months of age, both vaccine-type and non-vaccine-type carriage rates were similar among PCV10-vaccinated participants, PCV13-vaccinated participants and unvaccinated controls at 6 and 12 months of age. Based on preliminary data, a single dose of PCV at 2 months of age does not appear to reduce pneumococcal carriage during the first year of life in this population.
