Mimee Laddaphone, Laos
Lao-Oxford-Mahosot Hospital-Wellcome Trust Research Unit Microbiology LaboratoryAuthor Of 3 Presentations
COMMUNICATING PCV13 IMPACT RESULTS IN LAO PDR, USING A MULTIMEDIA APPROACH (ID 690)
- Shereen Labib, Australia
- Jocelyn Chan,
- Keoudomphone Vilivong, Laos
- Mimee Laddaphone, Laos
- Jana Y. Lai, Australia
- Lauren Franzel-Sassanpour, Laos
- Eileen M. Dunne, United States of America
- Paul N. Newton, United Kingdom
- Kim E. Mulholland, Australia
- Audrey Dubot-Pérès, Laos
- Catherine Satzke, Australia
- Molina Choummanivong, Laos
- Vanphanom Sychareun, Laos
- Anonh Xeuatvongsa, Laos
- Mayfong Mayxay, United Kingdom
- David A. Dance, Laos
- Fiona M. Russell, Australia
Abstract
Background
In 2013, Lao PDR introduced PCV13 with Gavi support. WHO requested a PCV13 impact evaluation as the Ministry of Health required evidence of PCV13 impact. Our project included a variety of community and hospital-based carriage and disease studies.
Methods
We partnered with Lao Ministry of Health and WHO, the key end-users, from the outset. We performed high quality research by collaborating with established international research institutions in Laos, the Lao Oxford Mahosot Hospital-Wellcome Trust Research Unit (LOMWRU) and the leading Lao medical university, The University of Health Sciences, to undertake the research. We developed an infographic and a video of the results.
Results
We disseminated our results to immunisation policy makers at the Lao Ministry of Health, WHO (Laos office and Geneva) and our funders, Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. Our results were presented to the Lao paediatricians and NITAG members; and at various local, regional and international conferences. The Laos Minister of Health presented the findings to the Gavi Board. The video and infographic were launched on social media and hosted on our institutions’ (MCRI and University of Melbourne) webpage, to coincide with World Pneumonia Day.
Conclusions
This multipronged approach ensured wide dissemination of findings.
NASOPHARYNGEAL PNEUMOCOCCAL DENSITY IS ASSOCIATED WITH SEVERE PNEUMONIA IN YOUNG CHILDREN IN LAO PDR (ID 856)
- Olivia J. Carr, Australia
- Keoudomphone Vilivong, Laos
- Mimee Laddaphone, Laos
- Eileen M. Dunne, United States of America
- Jana Y. Lai, Australia
- Jocelyn Chan,
- Malisa Vongsakid, Laos
- Chanthaphone Siladeth, Laos
- Belinda D. Ortika, Australia
- Mayfong Mayxay, United Kingdom
- Paul N. Newton, United Kingdom
- Lien Anh Ha H. Do, Australia
- Kim E. Mulholland, Australia
- Audrey Dubot-Pérès, Laos
- Catherine Satzke, Australia
- David A. Dance, Laos
- Fiona M. Russell, Australia
Abstract
Background
Pneumococcal nasopharyngeal colonisation density >6.9 log10 copies/mL is associated with primary endpoint pneumonia, very severe pneumonia and hypoxic pneumonia. Few studies have explored the association between pneumococcal density and severe pneumonia. We determined the association between nasopharyngeal pneumococcal density and children with severe pneumonia in Laos.
Methods
A prospective observational study was conducted at Mahosot Hospital. Children <5 years of age admitted with ARI were recruited (2014 to mid-2018). Clinical and demographic data were collected alongside with nasopharyngeal swabs. Severe pneumonia was classified according to the WHO 2013 definition. Pneumococci were detected and quantified by lytA qPCR. A logistic regression model deterimined the association between pneumococcal density and severe pneumonia, after adjusting for potential confounders.
Results
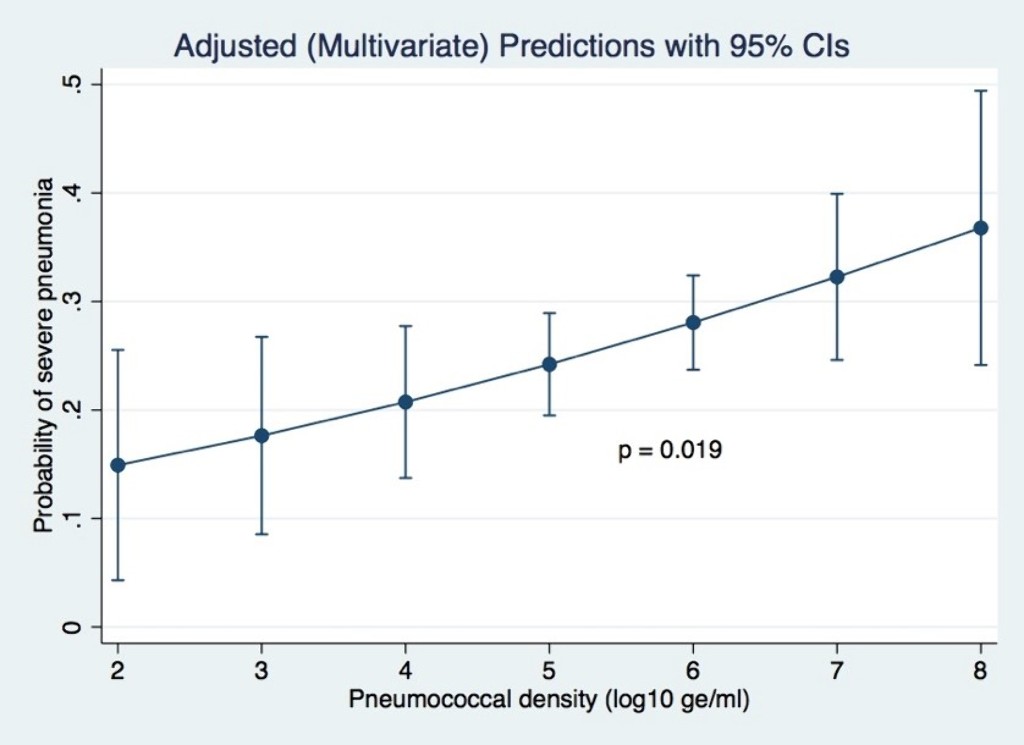
Of 1,289 participants enrolled, 32.2% had severe pneumonia. After adjusting for potential confounders (age, ethnicity, residential location, living with children <5 years, exposure to cigarette smoke, monthly income, PCV13 vaccination status and co-detection of RSV), pneumococcal density was positively associated with severe pneumonia (adjusted odds ratio 1.4; 95% CI 1.1–1.8; p=0.019).
Conclusions
Pneumococcal carriage density is associated with the probability of severe pneumonia in children in this setting.
PNEUMOCOCCAL CARRIAGE IN CHILDREN WITH PNEUMONIA IN THREE ASIAN COUNTRIES FOLLOWING VACCINE INTRODUCTION (ID 1082)
- Catherine Satzke, Australia
- Eileen M. Dunne, United States of America
- Jocelyn Chan,
- Monica L. Nation, Australia
- Keoudomphone Vilivong, Laos
- Belinda D. Ortika, Australia
- Mimee Laddaphone, Laos
- Rebecca Ford, Papua New Guinea
- Joycelyn J. Sapura, Papua New Guinea
- John Kave, Papua New Guinea
- Cattram D. Nguyen, Australia
- Casey L. Pell, Australia
- Ahmed Alamrousi, Australia
- Jason Hinds, United Kingdom
- Paul N. Newton, United Kingdom
- Anonh Xeuatvongsa, Laos
- B Bunjinlham,
- Christopher C. Blyth, Australia
- David A. Dance, Laos
- William Pomat, Papua New Guinea
- Claire Von Mollendorf, Australia
- Tuya Mungun, Mongolia
- Kim E. Mulholland, Australia
- Fiona M. Russell, Australia
