M. Haartmans (Maastricht, NL)
Maastricht University Orthopedic Surgery / M4iPresenter Of 1 Presentation
18.3.2 - Evaluation of the Effect of Celecoxib on Cartilage in Vitro and in a Rat Osteoarthritis Model
Abstract
Purpose
Celecoxib, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug and selective cyclooxygenase-II inhibitor, is used to reduce pain and inflammation in knee osteoarthritis patients. However, its potential protective effect on cartilage degeneration is disputed. In this study, we aimed to investigate the chondroprotective effect of celecoxib on cartilage-secreted molecules and gene expression in vitro, and its protective effect on cartilage in vivo.
Methods and Materials
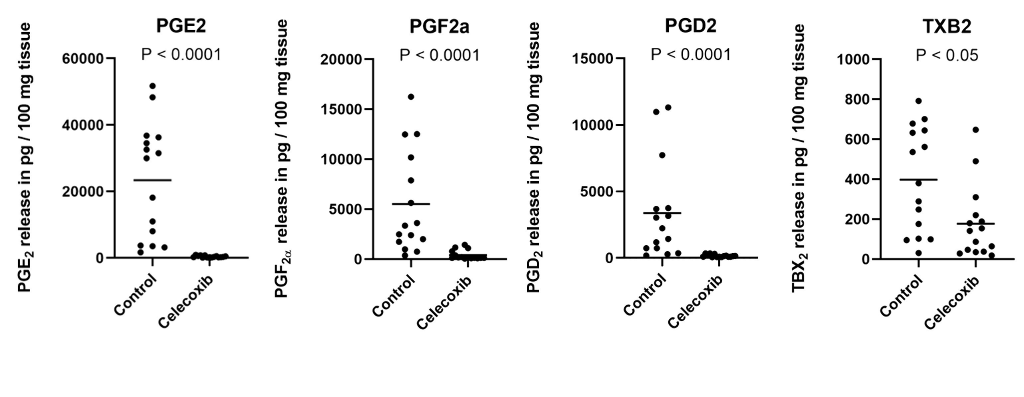
Sixteen articular cartilage explants (tibia and femur, MEC 08-04-028) from osteoarthritis patients cultured for 24 hours with 10µM celecoxib or dimethyl sulfoxide (v/v 1:1000, vehicle). Secreted prostaglandin (PGE2, PGF2α, PGD2 and TXB2) concentrations were determined by ELISA and secreted proteins were measured with label-free liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry in conditioned media. To determine celecoxib chondroprotective effects in vivo, an osteoarthritis rat model (ACLT/pMMx model, DEC13-052) was used to investigate cartilage osteoarthritis-related degeneration 4 weeks after an intra-articular injection of celecoxib or control (92.25ng celecoxib or 25μl 0.9% NaCl) treatment. Histopathological scoring was applied to score osteoarthritis severity 12 weeks after injection.
Results
PGE2 (23397 vs 387 pg/100mg), PGF2α (5500 vs 401 pg/100mg), PGD2 (3386 vs 159 pg/100mg) and TXB2 (397 vs 176 pg/100mg) release by cartilage explants was significantly reduced in the celecoxib treated group. Furthermore, mass spectrometry analysis revealed a significant increase of TIMP-2 and reduction of target of Nesh-SH3 and SPARC protein secreted by cartilage samples treated with celecoxib. In the in vivo study, cartilage degeneration in rat knees treated with celecoxib was significantly reduced (average OARSI score 4.9 (osteoarthritis) vs 1.9 (control)).

Conclusion
In this study, we found an anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective effect of celecoxib on cartilage in vitro, and a protective effect for cartilage degeneration in vivo. This will add hopeful information to the ongoing discussion on the conflicting results for celecoxib in the use for osteoarthritis treatment.



