
Serena Villaverde (Spain)
HOSPITAL 12 DE OCTUBRE PAEDIATRICSAuthor Of 4 Presentations
ANTIBODY KINETICS AND CLINICAL OUTCOMES IN A COHORT OF INFANTS BORN FROM MOTHERS WITH SARS-COV-2 INFECTION DURING PREGNANCY (CORONASCOPE STUDY)
Abstract
Backgrounds:
We aim to describe outcomes (focusing on hearing and neurological findings) and transfer of maternal antibodies in infants born from mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy.
Methods:
Observational prospective study performed in a tertiary hospital in Madrid (Spain). Infants born from mothers with SARS CoV-2 infection during pregnancy from March to September 2020 were included. SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCT on nasopharyngeal swab (NPS) was performed at birth to infants born from mother with acute infection at delivery. A follow-up visit with physical and neurological examination, SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR on NPS, SARS-CoV-2 serology, and a cranial ultrasound (cUS) was performed within 3 months of life. Automated auditory brainstem response (A-ABR) exams were performed at birth, and auditory steady-state response (ASSR) at six months of life.
Results:
95 infants born from 94 mothers were included. Median gestational age was 39+3 (IQR 38-40) and 10 (10.5%) were preterm. Thirteen (13.7%) newborns required hospital admission after birth, none of them with a COVID-19 infection. Rates of vertical (1/28; 3.6%) and horizontal (1/93; 1.1%) transmitted infections were low, with mild symptoms. In follow-up visit, neurological examination was normal in all infants. Cranial ultrasound was normal in 81/85 (95.3%) infants, with mild abnormalities in four infants. 47/ 95 (50%) infants had a positive serology. Serology result was not related to the severity of the maternal infection, skin-to-skin care at birth or breastfeeding. There was a progressive decrease in SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers with the age (figure 1). No hearing loss was detected.

Conclusions/Learning Points:
In this cohort, most infants born from mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy had normal cUS, hearing screening and neurological examinations in the follow-up. There is a rapid decrease in transferred maternal antibodies in the first months of life.
IMPACT IN ANTIBIOTIC USE AFTER IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP PROGRAM AND A JOINT PROTOCOL WITH ELECTRONIC PRESCRIPTION FOR APPENDICITIS/PERITONITIS IN PEDIATRICS
Abstract
Backgrounds:
Initial antibiotic treatment in appendicitis/peritonitis significantly reduces wound infection and intra-abdominal abscess formation in patients with gangrenous or perforated appendicitis. Randomized controlled trials have shown that the use of lower-spectrum antibiotic combinations is as effective in preventing abscesses or surgical wound infections as broad-spectrum regimens.
Methods
Observational, retrospective study of patients <16 years of age admitted for appendicitis and/or peritonitis from Jan/2014 to Dec/2019 in a tertiary university hospital in Madrid, Spain. Three study periods were established: P1 2014-2015 (before Antimicrobial Stewardship Programme (ASP)), P2 2016-2018 (ASP implemented) and P3 Jan/2019-Dec/2019 (ASP and implementation of an appendicitis/peritonitis protocol with electronic prescription, including lower-spectrum antibiotic combinations and selected and clinically guided use after surgery). Antimicrobial use was analysed with the days of therapy/1000 admissions days (DOT/1000) and start of treatment/1000 hospital admissions (SOT/1000).
Results:
During the study period a total of 1619 patients met inclusion criteria. The proportion of patients without antibiotic therapy after surgery during P1, P2 and P3 was 5.6%, 3.7%, and 38.6% respectively. [C1] The evolution of antibiotic use expressed by DOT / 1000 is shown in Figure 1. SOT/1000 of ampicillin, gentamicin and metronidazole rose from 162, 190 and 190 in 2014 to 386, 402 and 409 in 2019. DOT/1000 of meropenem drop to 64.85 in 2014 to 0 in 2019.

Conclusions/Learning Points:
The implementation of an ASP and a low-spectrum antibiotic protocol with electronic prescribing, reduced the antimicrobial use in children with appendicitis/peritonitis. The proportion of patients without antibiotic therapy after surgery increased and the use of carbapenems and other broad-spectrum antibiotics was reduced after the intervention. These improvements were observed when an electronically available protocol was added to the ASP implementation.
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND OUTCOMES OF GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTEREMIA IN A TERTIARY UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL IN MADRID, SPAIN (2018-2020).
Abstract
Backgrounds:
Gram-negative bacteremia (GNB) is associated with a significant rate of morbidity and mortality in adults. Moreover, resistances to antibiotics are increasingly described in surveillance reports. However, the epidemiology and outcomes of GNB in children are not well known. We aimed to analyze GNB bacteremia in pediatric patients in a tertiary hospital over a three years period.
Methods
A retrospective, observational study of bacteremia episodes caused by Enterobacteriaceae or non-fermentative GNB in pediatric patients between January of 2018 and December 2020 in a Tertiary Hospital from Madrid, Spain, was carried out through microbiology charts and clinical records. Demography, comorbidities, risk factors and infection characteristics were recorded, and bacterial strain and antibiotic resistance were registered. Three primary endpoints were defined: mortality, bacteremia persistence and recurrence. A statistical analysis was applied to assess differences in these outcomes according to the risk factors. A multivariable logistic regression analysis was used to assess the association between bacteria resistance and mortality.
Results:
One hundred eighteen cases of GNB in one hundred and seven patients were included. The characteristics of the patients are shown in Table 1. In fifty-three cases (44.9%) GNB presented resistance to at least one group of antibiotic and in nine (7.6%) were multidrug-resistant (Table 1). The incidence of resistance rates by years were stable. Indwelling urinary catheterization was a risk factor associated to mortality [OR 3.48 (1.20-10.6)] and parenteral nutrition was related to persistent bacteremia [OR 7.69 (1.1-209)]. No relation between drug resistance and mortality was observed in multivariable analysis.

Conclusions/Learning Points:
GNB represented an important problem in our institution, mainly related to neonatal intensive care and heart surgery. Antibiotic resistance was common. Patients that carried invasive care devices presented higher rates of bacteremia persistence and mortality.
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF A BREATH-RATE MEASUREMENT SOLUTION BASED ON COMPUTER VISION AND MACHINE LEARNING TECHNIQUES IN CHILDREN WITH LOWER RESPIRATORY INFECTION
Abstract
Backgrounds:
Camera-based diagnostic methods could allow an objective analysis of a patient's health remotely and contactless, which is especially interesting in telemedicine and pandemic scenarios. Artificial intelligence and computer vision can provide the diagnostic tools needed to improve patient monitoring. The main objective of this work is the design and implementation of a solution to estimate respiratory rate (RR) from a video captured through a smartphone, based on computer vision and deep learning techniques.
Methods
Prospective study of clinical information and a video of the patients’ chest with and without respiratory distress under 10 years old from November 2020 to May 2021 attending for a lower respiratory infection in a tertiary hospital in Spain. Video pre-processing was carried out using computer vision methods. As an initial approximation, remote photoplethysmographic signal (rPPG) was used with subsequent processing using the Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) and different methods to estimate the RR.
Results:
19 patients were included and 22 video sequences were pre-processed to carry out the estimation of the respiratory rate using the PPG signal approach. 51.3% were males and the average rate age was 2 years (DE 0.32). 61.5% patients had not relevant medical records. 48.7% were diagnosed of bronchiolitis followed by 30.1% diagnosed of asthma symptoms. Results obtained by different methods to estimate the RR can be seen in Table 1.
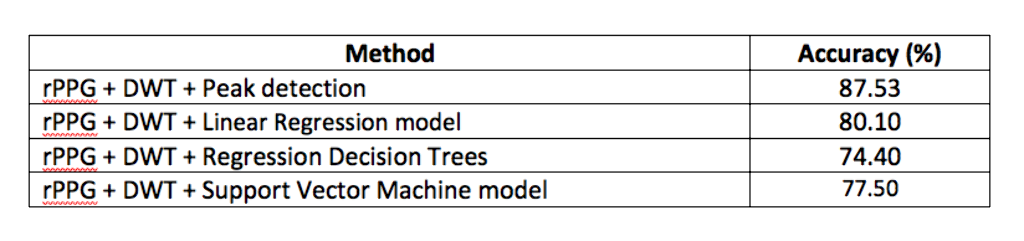
Conclusions/Learning Points:
It has been possible to design a breath-rate measurement solution to estimate RR from a video, based on DWT transformation to rPPG signal. This could be the first step in order to implement a breath-rate measurement solution based on computer vision and deep learning techniques.
Presenter of 2 Presentations
IMPACT IN ANTIBIOTIC USE AFTER IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP PROGRAM AND A JOINT PROTOCOL WITH ELECTRONIC PRESCRIPTION FOR APPENDICITIS/PERITONITIS IN PEDIATRICS
Abstract
Backgrounds:
Initial antibiotic treatment in appendicitis/peritonitis significantly reduces wound infection and intra-abdominal abscess formation in patients with gangrenous or perforated appendicitis. Randomized controlled trials have shown that the use of lower-spectrum antibiotic combinations is as effective in preventing abscesses or surgical wound infections as broad-spectrum regimens.
Methods
Observational, retrospective study of patients <16 years of age admitted for appendicitis and/or peritonitis from Jan/2014 to Dec/2019 in a tertiary university hospital in Madrid, Spain. Three study periods were established: P1 2014-2015 (before Antimicrobial Stewardship Programme (ASP)), P2 2016-2018 (ASP implemented) and P3 Jan/2019-Dec/2019 (ASP and implementation of an appendicitis/peritonitis protocol with electronic prescription, including lower-spectrum antibiotic combinations and selected and clinically guided use after surgery). Antimicrobial use was analysed with the days of therapy/1000 admissions days (DOT/1000) and start of treatment/1000 hospital admissions (SOT/1000).
Results:
During the study period a total of 1619 patients met inclusion criteria. The proportion of patients without antibiotic therapy after surgery during P1, P2 and P3 was 5.6%, 3.7%, and 38.6% respectively. [C1] The evolution of antibiotic use expressed by DOT / 1000 is shown in Figure 1. SOT/1000 of ampicillin, gentamicin and metronidazole rose from 162, 190 and 190 in 2014 to 386, 402 and 409 in 2019. DOT/1000 of meropenem drop to 64.85 in 2014 to 0 in 2019.

Conclusions/Learning Points:
The implementation of an ASP and a low-spectrum antibiotic protocol with electronic prescribing, reduced the antimicrobial use in children with appendicitis/peritonitis. The proportion of patients without antibiotic therapy after surgery increased and the use of carbapenems and other broad-spectrum antibiotics was reduced after the intervention. These improvements were observed when an electronically available protocol was added to the ASP implementation.
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF A BREATH-RATE MEASUREMENT SOLUTION BASED ON COMPUTER VISION AND MACHINE LEARNING TECHNIQUES IN CHILDREN WITH LOWER RESPIRATORY INFECTION
Abstract
Backgrounds:
Camera-based diagnostic methods could allow an objective analysis of a patient's health remotely and contactless, which is especially interesting in telemedicine and pandemic scenarios. Artificial intelligence and computer vision can provide the diagnostic tools needed to improve patient monitoring. The main objective of this work is the design and implementation of a solution to estimate respiratory rate (RR) from a video captured through a smartphone, based on computer vision and deep learning techniques.
Methods
Prospective study of clinical information and a video of the patients’ chest with and without respiratory distress under 10 years old from November 2020 to May 2021 attending for a lower respiratory infection in a tertiary hospital in Spain. Video pre-processing was carried out using computer vision methods. As an initial approximation, remote photoplethysmographic signal (rPPG) was used with subsequent processing using the Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) and different methods to estimate the RR.
Results:
19 patients were included and 22 video sequences were pre-processed to carry out the estimation of the respiratory rate using the PPG signal approach. 51.3% were males and the average rate age was 2 years (DE 0.32). 61.5% patients had not relevant medical records. 48.7% were diagnosed of bronchiolitis followed by 30.1% diagnosed of asthma symptoms. Results obtained by different methods to estimate the RR can be seen in Table 1.

Conclusions/Learning Points:
It has been possible to design a breath-rate measurement solution to estimate RR from a video, based on DWT transformation to rPPG signal. This could be the first step in order to implement a breath-rate measurement solution based on computer vision and deep learning techniques.
Poster Author Of 5 e-Posters
EP338 - CONCORDANCE ON RESPIRATORY RATE EVALUATED THROUGH A VIDEO RECORDING IN CHILDREN WITH LOWER RESPIRATORY INFECTION (ID 1177)
EP484 - PAPILLEDEMA IN PATIENTS WITH MULTISYSTEM INFLAMMATORY SYNDROME: IS AN OPHTALMOLOGICAL EXAM USEFUL? (ID 360)
- Alberto Muñoz (Spain)
- Ana Ortueta (Spain)
- Cristina Lopez (Spain)
- Sara Domínguez (Spain)
- Elisa Fernandez (Spain)
- Cinta Moraleda (Spain)
- Daniel Blázquez-Gamero (Spain)
- Luis Prieto (Spain)
- Jaime Carrasco (Spain)
- Angela Manzanares (Spain)
- David Torres (Spain)
- Serena Villaverde (Spain)
- Pablo Rojo (Spain)
- Cristina Epalza (Spain)
PD091 - CLINICAL IMPACT AFTER IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP PROGRAM AND A JOINT ELECTRONIC PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH APPENDICITIS AND/OR PERITONITIS IN PEDIATRICS (ID 775)
- Serena Villaverde (Spain)
- Patricia Brañas (Spain)
- José Manuel Caro (Spain)
- Rocío Morante (Spain)
- Irene Gómez (Spain)
- Gloria Mirete (Spain)
- Cinta Moraleda (Spain)
- Daniel Blázquez-Gamero (Spain)
- Angela Manzanares (Spain)
- David Torres (Spain)
- Elisa Fernandez (Spain)
- Luis Prieto (Spain)
- Pablo Rojo (Spain)
- Cristina Epalza (Spain)
PD101 - MICROBIOLOGICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF CLINICAL ISOLATES IN PEDIATRIC APPENDICITIS DURING AN ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP PROGRAM IN A TERTIARY HOSPITAL IN MADRID, SPAIN (ID 778)
PD113 - LONG TERM ESTHETIC AND FUNCTIONAL OUTCOMES IN CHILDREN WITH NONTUBERCULOUS MYCOBACTERIAL LYMPHADENITIS (ID 1289)
- Angela Manzanares (Spain)
- Marta Nabal (Spain)
- María Collada (Spain)
- Carmen González (Spain)
- Estrella Esquivel (Spain)
- María Dolores Delgado (Spain)
- Eunate Martí (Spain)
- Jesús Redondo (Spain)
- Paula López-Roa (Spain)
- Nuria Alberti (Spain)
- Elisa Fernandez-Cooke (Spain)
- Luis Prieto (Spain)
- Cinta Moraleda (Spain)
- Cristina Epalza (Spain)
- Serena Villaverde (Spain)
- Pablo Rojo (Spain)
- Daniel Blázquez-Gamero (Spain)





